October 21, 2025
Download:
Near Record High Investment in U.S. Broadband Infrastructure Continues as Industry Embraces AI, Advanced Tech Era
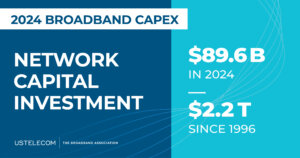
Providers Invested Nearly $90 Billion in Communications Infrastructure in 2024
America’s broadband providers invested $89.6 billion in U.S. communications infrastructure in 2024. The continued strong pace of investment, topping $2.2 trillion since 1996, underscores broadband’s essential role in powering the U.S. economy at the dawning age of artificial intelligence.
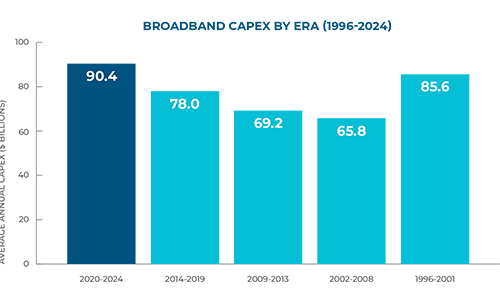
The Broadband Investment Journey
Over the past three decades, broadband investment has evolved through distinct eras of growth, adaptation, and innovation:
- 1996–2001: Light-Touch Regulation & Dot-Com Boom – Surging investment after 1996 Telecom Act.
- 2002–2008: Stabilization, Early Broadband & Mobility Advancement – Restructuring, early adoption of broadband, and rapid wireless expansion.
- 2009–2013: Start of the Streaming Era & Smartphone Surge – Growing demand for streaming video, smartphones and mobile connectivity, contrasting sluggish general economic investment.
- 2014–2019: Fiber & Wireless Densification – Expansion of fiber, LTE and small cells laid groundwork for next-generation networks.
- 2020–2024: Remote Connectivity, 5G & AI Era – Historic highs driven by remote work, cloud applications, and first wave of AI-era capacity needs.
Broadband providers have steadily invested tens of billions of dollars annually expanding and modernizing U.S. networks to meet rising connectivity demands and keep our nation at the forefront of the global digital economy.
Each investment era reflects changing demand drivers — from early broadband adoption, to mobile and streaming, and now artificial intelligence. Investment at scale is closely tied to policy stability: when regulation supports long-term planning and investment, capital flows into network upgrades.
Cumulative investment of more than $2.2 trillion since 1996 places broadband among America’s most capital-intensive industries, with broadband’s share of revenues reinvested in world-class networks far outpacing most consumer industries. This underscores the central role of private capital and pro-investment policies in building the infrastructure powering today’s economy and tomorrow’s AI-driven innovations.
The Bottom Line
In 2024, capital spending reflected long-term trends supporting the evolution of the nation’s connectivity infrastructure: deeper fiber deployment, expanding rural reach, wireless development, and growing overall network capacity to support booming AI, cloud computing, streaming and other advances.
At the same time, providers navigated headwinds in 2024 — including higher interest rates and a more cautious capital expenditure environment. Providers also focused on operational efficiencies and drew down on stockpiles of equipment acquired during supply chain shortages. Even so, competition and strong demand for connectivity sustained 2024’s near-record investment levels.
Methodology
This USTelecom report collects capital expenditures data for major wireline, wireless, and cable broadband providers to approximate an industry aggregate. This figure does not include smaller wireline broadband providers, electric cooperatives, or satellite broadband providers due to the difficulty of obtaining consistent and comparable data. We estimate these competitors’ capex contributions at no less than $2 billion. Thus, the $89.6 billion annual capex figure in this report is a conservative estimate.