October 31, 2017
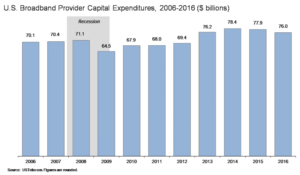
Investment in U.S. broadband networks continued to slide in 2016, continuing a trend that began two years ago after the Federal Communications Commission reclassified broadband providers as common carriers under Title II of the Communications Act. U.S. broadband providers invested approximately $76 billion in capital expenditures on network infrastructure in 2016, down from approximately $77.9 billion in 2015, according to USTelecom’s seventh annual broadband investment research report released today.
Annual spending was $2.4 billion less in 2016 than at the recent peak of $78.4 billion in 2014, according to the analysis. Overall, from 1996 through 2016, the broadband industry has made capital investments totaling $1.6 trillion.
USTelecom’s data series stretches back 21 years, including years of growth and some declines as broadband providers – from wireline and wireless to cable companies – have invested in maintaining, improving or expanding their U.S. networks. Because USTelecom’s analysis attempts to consistently measure infrastructure spending from year to year, it adjusts for many factors that affect companies’ capital investment reporting, including mergers, divestments, accounting practices, and allocations among business units. (Please see the report’s methodology for more details on how the figures were calculated.)
The data include minor historical revisions to the time series. USTelecom’s revised estimates indicate that industry capital expenditures fell by approximately a half billion dollars from 2014 to 2015 and by nearly $2 billion from 2015 to 2016. The start of the decline – the first since the recession ended in 2009 – coincided with FCC’s 2015 decision to adopt the Open Internet Order.
![]()
Many factors affect capital spending, such as competition, financial markets, taxes, government mandates, project timelines, and regulation. In this research brief, USTelecom does not attempt to isolate and control for the various factors and therefore does not draw conclusions about the extent to which Title II may have caused the decline in capital investment.
Nevertheless, the two-year investment decline clearly raises questions about the impact that the FCC’s open internet regulations may have had on overall industry broadband investment, which warrants further investigation and analysis.
Broadband investment remains critical to modernizing our nation’s network infrastructure and maintaining our international leadership. Getting the policy right will be critical given the projected growth of consumer demand for broadband access.